Custom Endpoints
Conduit attempts to help you cut back on boilerplate code.
Besides offering support for optional auto-generated CRUD endpoints for your custom schemas,
it also provides the means for you to construct powerful functional endpoints,
allowing you to effortlessly operate on your backend without having to write any code whatsoever.
These endpoints are schema-based, meaning they make use of a specific schema's entries.
Both system and custom schemas are supported.
Creating Endpoints
Bring up the Admin Panel and navigate to the Database section.
Then head to the Custom Endpoints tab.
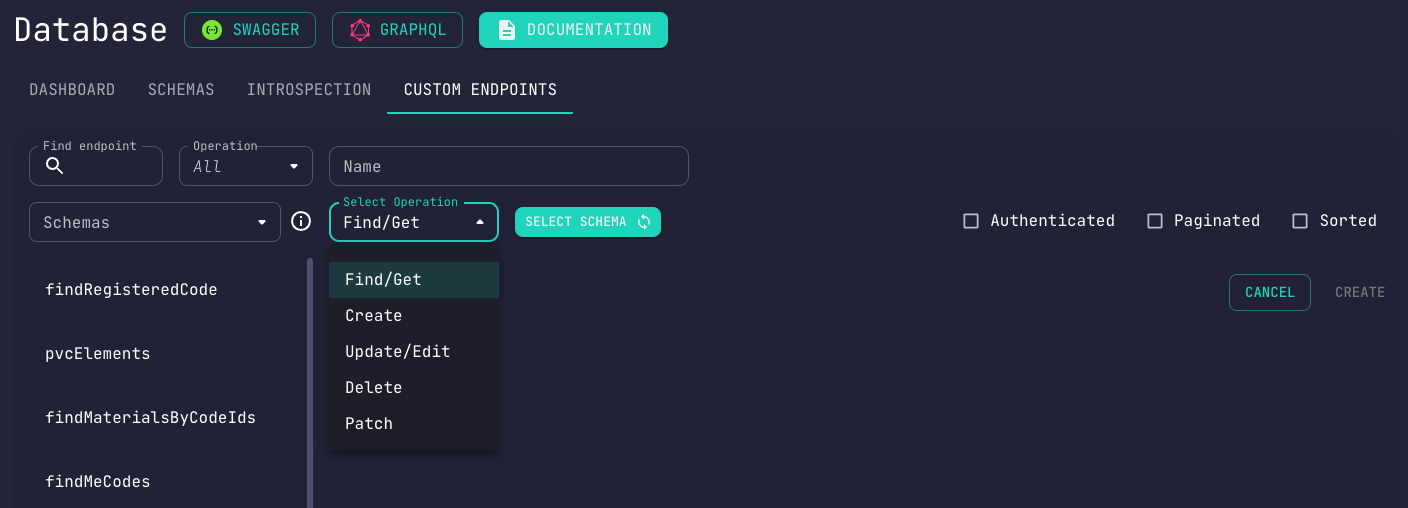
Let's show you around the place.
Here's a rundown of the base fields and options making up a custom endpoint:
Nameto be used as the endpoint's nameAuthenticateddefines whether endpoint requires user authenticationOperationto be used for the endpointSchemato be used for the endpoint
Find/Get operations additionally offer the following options:
Paginateddefines whether endpoint should provide pagination (skip/limit)Sorteddefines whether results should be sorted
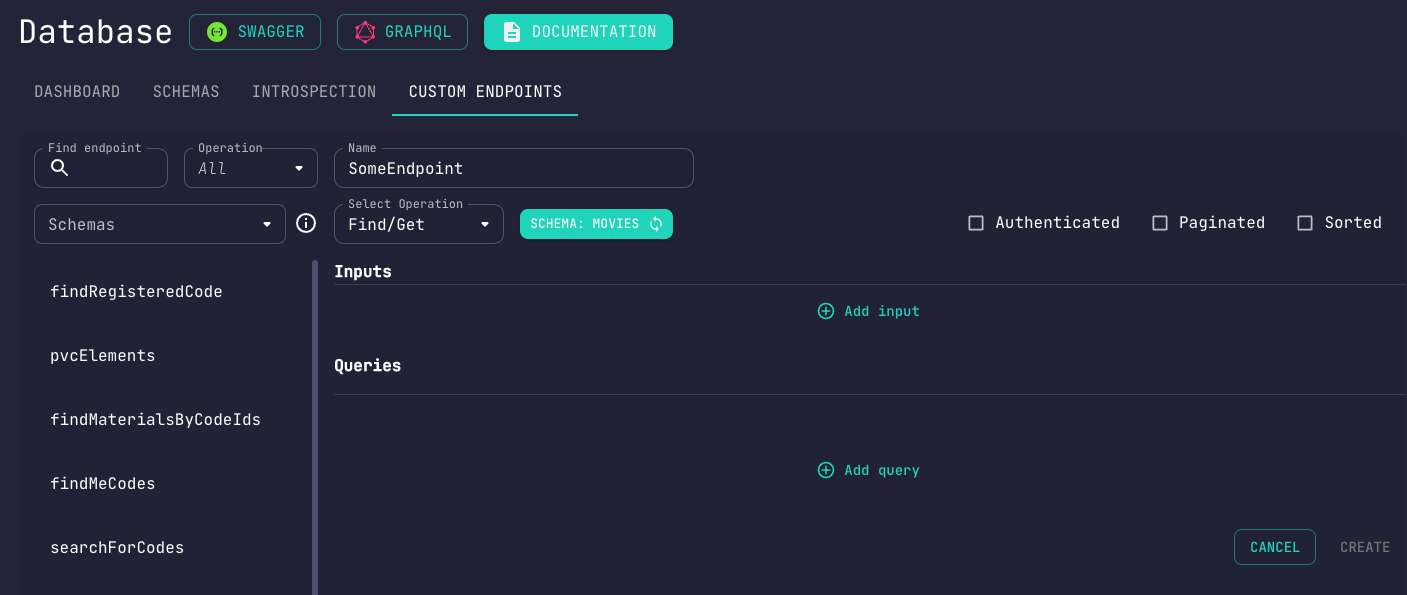
Upon selecting your request type, the page is updated with the appropriate sections to be used while defining your endpoint's behavior.
Inputs
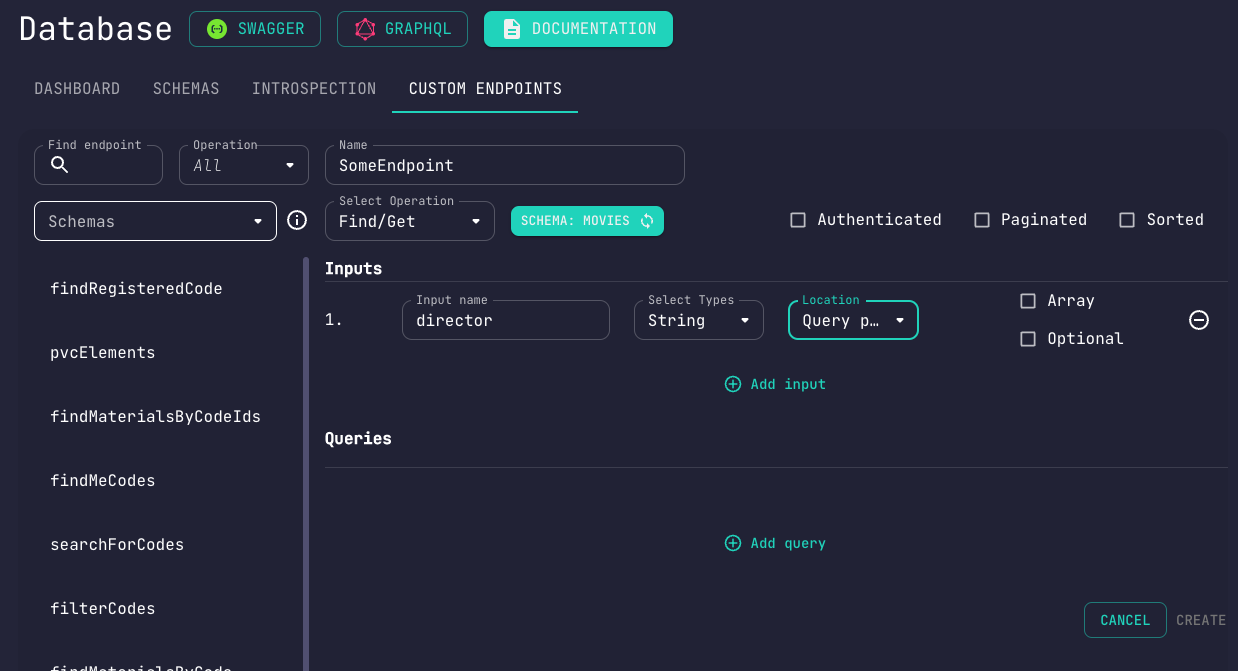
If you wish to, you may conditionally operate on your data based on variable fields.
Here's what makes up an input:
Nameto be used while referring to this field in the followup sectionsTypespecifies the type of the fieldLocationdefines whether the field should be a query, body or url paramArraydefines whether the field should be an arrayOptionaldefines whether the field should be optional
Queries
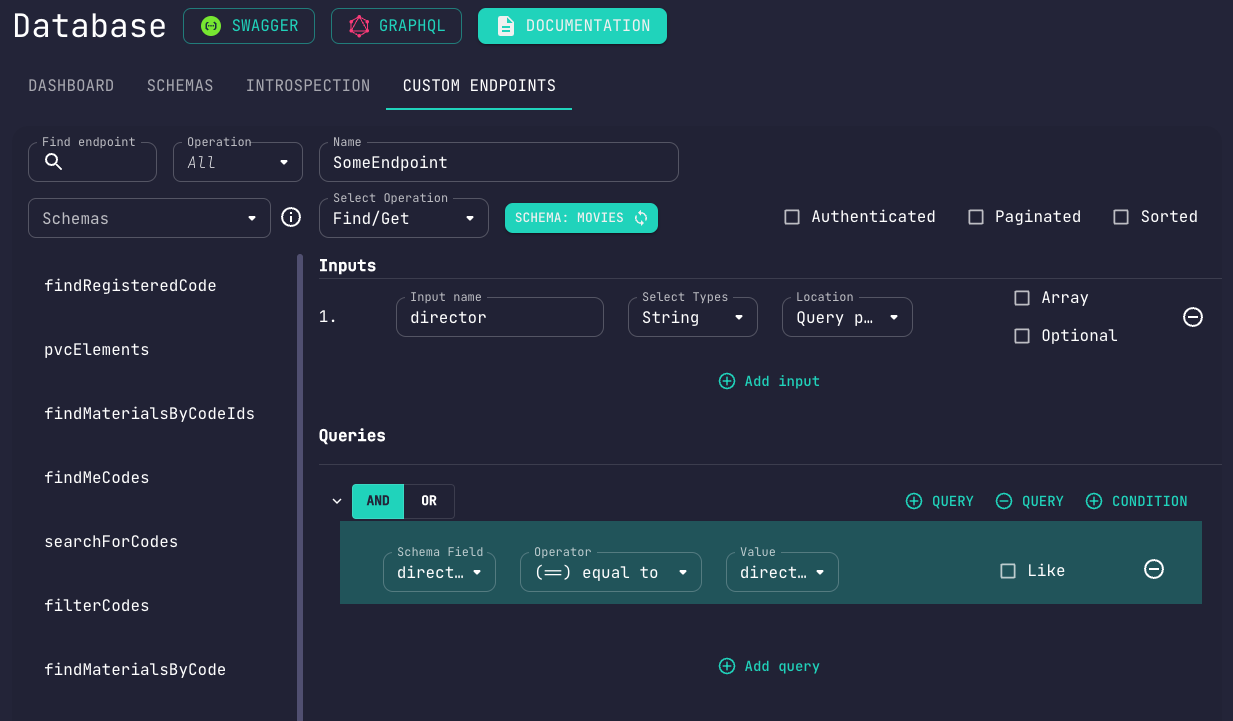
You're going to have to specify at least one query condition for your endpoint.
Queries require a schema field to be compared against as well as a condition,
comparing that field to a specific value (or a set of values).
These values may be defined through any of the following:
System Valuesare internal context values (middleware-dependent)Custom Valuesmay be provided during endpoint creation (hardcoded)Schema Fieldsare existing fields from the target schemaInput Fieldsare defined in theInputssection
The SQL-style Like operator is also supported.
Query condition checks can be ANDed or ORed.
They may also be nested however you see fit.
Assignments
While creating or updating a schema doc entry, you're going to have to specify the values for your schema fields.
Create and Update/Edit operations require that you specify all schema fields,
whereas Patch ones let you partially update an existing schema document.
Assignment definitions include the following fields:
Schema Fieldto be populatedActionto be used for the operationAssignment Valueto be used while populating the field
A field may be populated through any of the following actions:
SETpopulates the field with target assignment valueINCREMENTincrements the field by target assignment valueDECREMENTdecrements the field by target assignment valueAPPENDappends the target assignment value to an array fieldREMOVEremoves the target assignment value from an array field
Similarly to how Queries operate, assignment values may come from:
- request context
- inputs (specified in the Inputs section)
- custom values